CITE-sort
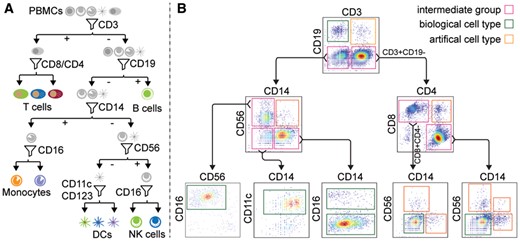
CITE-sort is an artificial-cell-type aware surface marker clustering method for CITE-seq. CITE-sort is aware of and is robust to multiplet-induced ACT. We benchmarked CITE-sort with real and simulated CITE-seq datasets and compared CITE-sort against canonical clustering methods. We show that CITE-sort produces the best clustering performance across the board. CITE-sort not only accurately identifies real biological cell types (BCT) but also consistently and reliably separates multiplet-induced artificial-cell-type droplet clusters from real BCT droplet clusters. In addition, CITE-sort organizes its clustering process with a binary tree, which facilitates easy interpretation and verification of its clustering result and simplifies cell-type annotation with domain knowledge in CITE-seq.
Paper
Github
Docs